Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of digital commerce, ensuring the accuracy of payment authorizations has become a critical necessity for businesses. Payment Authorization Management (PAM) encompasses the application of cutting-edge technology, specialized expertise, robust data analytics, and streamlined processes. These elements work in tandem to enhance the accuracy of payment authorization decisions, ultimately increasing the volume of legitimate transactions processed between merchants and customers.
Understanding the Payment Authorization Ecosystem
The card payments authorization ecosystem is a complex network involving three primary stakeholders:
- Merchants: Businesses that offer products and services to consumers.
- Customers: Individuals or entities purchasing these goods or services.
- Banks and Payment Authorization Systems: These entities, including fraud protection systems, are responsible for determining whether each transaction request is approved or declined.
The core objective of this ecosystem is straightforward yet intricate: approve all legitimate payment transactions while declining fraudulent or otherwise undesirable requests. Given the scale and complexity of this system, which processes billions of legitimate and fraudulent requests in mere milliseconds, the need for accurate and swift decision-making is paramount.
However, the ecosystem operates in an increasingly dynamic environment. New sales channels and digital business models continually emerge, while the threat landscape from bad actors and sophisticated cybercriminals grows ever more daunting. This reality underscores the pressing need for advanced solutions to address the challenges faced by the payment authorization system.
Challenges Facing the Payment Authorization System
The payment authorization system is grappling with several new challenges that have emerged as a result of the digital age:
- Proliferation of Transactions: The explosion of digital devices has led to a significant increase in transaction volume.
- Evolving Transaction Types: The gig economy and other new business models have introduced novel transaction types that were not previously accounted for in traditional systems.
- Shifts in Purchase Patterns: The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the transition from in-person to eCommerce and other card-not-present (CNP) purchases.
- Growth in Recurring Billing: Both consumers and businesses are increasingly adopting recurring billing models, adding another layer of complexity.
- Data Breaches: Massive breaches have exposed vast amounts of user identities and credit data, empowering cybercriminals with the tools needed to perpetrate fraud.
These challenges, coupled with the inherent structural limitations of the payment authorization ecosystem, hinder the system’s ability to make accurate decisions.
Core Issues in Payment Authorization
The effectiveness of the payment authorization ecosystem is limited by several core challenges:
Misaligned Authorization Decision Goals: Banks, burdened with enormous losses from fraudulent transactions—estimated at $28.6 billion—often bias their fraud detection systems toward loss avoidance. This overcompensation leads to false declines, where legitimate transactions are wrongly rejected based on loosely associated factors rather than direct fraud signals.
Constraints on Authorization Decision Accuracy: The sophisticated systems banks and third-party companies have developed are only as effective as the information they are provided. Given the short timeframes in which these decisions must be made, combined with limitations on information access, the accuracy of these decisions is significantly constrained.
These issues manifest in two primary forms of costly errors:
- Approval of Fraudulent Transactions: This results in direct financial losses for banks and chargebacks for merchants.
- Decline of Legitimate Transactions: Known as false declines, these errors cause significant pain for merchants and customers alike.
While the costs of fraud losses are well-documented, the impact of false declines is less understood, primarily because this burden is distributed across millions of merchants and customers.
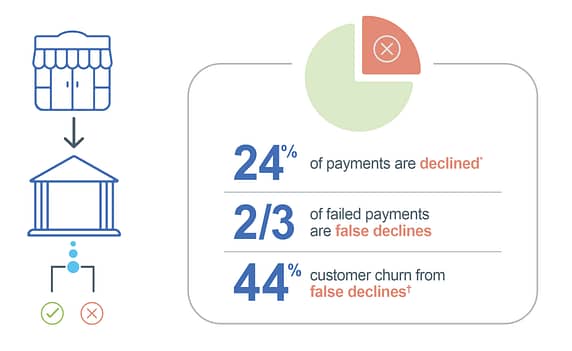
Beyond fraud-related declines, payment requests can also be declined for a variety of reasons, including insufficient funds, data issues, system incompatibilities, and payment gateway errors. These failed payments and false declines pose a significant problem for merchants, imposing opportunity costs that far exceed the direct losses associated with fraud.
According to the Aite Group, global false declines alone are expected to cost merchants over $443 billion in lost revenue from payment decline decisions in 2021.

A Closer Look at Authorization Decision Errors
False declines are not evenly distributed across all merchants or transaction types. Research conducted by Visa and Walmart indicates that payment authorization systems apply stricter criteria to CNP transactions, given the higher incidence of fraud associated with eCommerce and other non-physical transaction types. As a result, CNP transactions experience a much higher rate of failed payments compared to in-person transactions.
This issue is particularly detrimental to subscription-based businesses that rely on recurring billing models. False declines in these scenarios not only disrupt service delivery but also lead to customer churn. Payment failures account for up to 48% of customer churn in subscription businesses. This interruption in service delivery negatively impacts both the merchant and the customer:

- Merchant Impact: Profitable customer acquisition depends on achieving a minimum number of successful billing cycles and reaching a certain lifetime value (LTV) before turning a profit. Failed payments interrupt this revenue stream, reducing profitability and limiting the customer acquisition cost (CAC) that companies can afford to invest.
- Customer Impact: The convenience that customers expect from subscription services is compromised, leading to dissatisfaction and potential churn.
The Role of Payment Authorization Management (PAM)
Payment Authorization Management (PAM) refers to the FinTech solutions designed to enhance the accuracy of payment authorization decisions. These solutions aim to reduce fraudulent transactions, approve more legitimate transactions, and recover revenue lost due to failed payments.
PAM solutions function as a middle layer within the payment ecosystem, positioned between merchants, customers, and payment authorizers. By operating outside the traditional payment system, PAM solutions can supplement decision accuracy, reduce errors, and help close the gap toward achieving 100% completion of legitimate transactions.
PAM addresses systemic limitations in the payment authorization process by leveraging data, technology, and processes to improve decision-making. The complexity of fraud prevention algorithms and the sophisticated tactics employed by cybercriminals make payment decision errors inevitable. However, PAM solutions, powered by artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), are uniquely equipped to tackle these challenges.
Unlike rules-based systems that apply the same criteria to every transaction, AI and ML-driven PAM solutions can adapt to the specific nuances of each transaction. This adaptability is crucial for reducing decision errors and improving overall system performance.
Best Practices in PAM Implementation
Effective PAM solutions incorporate several best practices to optimize payment authorization accuracy:
- AI/Machine Learning Technology: These solutions autonomously create individualized payment submission strategies tailored to each transaction.
- Giga Datasets: Algorithms are trained on vast datasets containing billions of authorization records, encompassing both accurate and inaccurate decisions.
- Ecosystem Knowledge: Algorithms are coded with in-depth knowledge of the payment ecosystem to deliver improved authorization results.
- Cloud-Based Solutions: These solutions are supported by broad API capabilities, enabling easy integration with payment gateways and CRM/billing systems. This ensures the scalability and interoperability required for major networks.
- Customer Experience: PAM solutions are designed to be invisible to the end customer, eliminating the need for customer involvement in resolving payment issues. This approach prevents the negative experiences that can lead to customer churn.

While some companies have developed simplistic solutions to address authorization decision errors, particularly for false declines, these approaches are often insufficient. Rules-based or manual dunning solutions fall short of the performance levels that true PAM solutions, powered by AI and ML, can achieve.

Conclusion
The efficiency of the payment ecosystem is crucial for ensuring seamless purchase settlements for all legitimate transactions. For merchants, adopting a robust Payment Authorization Management (PAM) strategy is essential to minimizing friction and maximizing growth and profitability.
The challenges posed by inaccuracies in the payment authorization system are substantial, especially given the high volume of transactions processed through the system. This impact is even more pronounced for eCommerce and subscription-based businesses that rely on recurring billing models.
To overcome these challenges, merchants must embrace new technologies and solutions. Manual processes and simplistic rules-based approaches are no longer sufficient to address the complexities of modern payment systems. Instead, AI and advanced ML-powered PAM solutions offer the best path forward, delivering payment settlement success that is invisible to the customer and reducing the risk of customer churn caused by false declines.
Is your business experiencing failed recurring payments? Contact us today to explore solutions that will recover up to 80% of your failed recurring payments, increasing your cash flow and profitability.

